How to Design Multi-Lingual Entity
Introduction
If you want to open up to the global market these days, end-to-end localization is a must. ABP provides an already established infrastructure for static texts. However, this may not be sufficient for many applications. You may need to fully customize your app for a particular language and region.
Let's take a look at a few quotes from Christian Arno's article "How Foreign-Language Internet Strategies Boost Sales" to better understand the impact of this:
82% of European consumers are less likely to buy online if the site is not in their native tongue (Eurobarometer survey).
72.4% of global consumers are more likely to buy a product if the information is available in their own language (Common Sense Advisory).
The English language currently only accounts for 31% of all online use, and more than half of all searches are in languages other than English.
Today, 42% of all Internet users are in Asia, while almost one-quarter are in Europe and just over 10% are in Latin America.
Foreign languages have experienced exponential growth in online usage in the past decade -- with Chinese now officially the second-most-prominent-language on the Web. Arabic has increased by a whopping 2500%, while English has only risen by 204%
If you are looking for ways to expand your market share by fully customizing your application for a particular language and region, in this article I will explain how you can do it with ABP framework.
Source Code
You can find the source code of the application at abpframework/abp-samples.
Demo of the Final Application
At the end of this article, we will have created an application same as in the gif below.
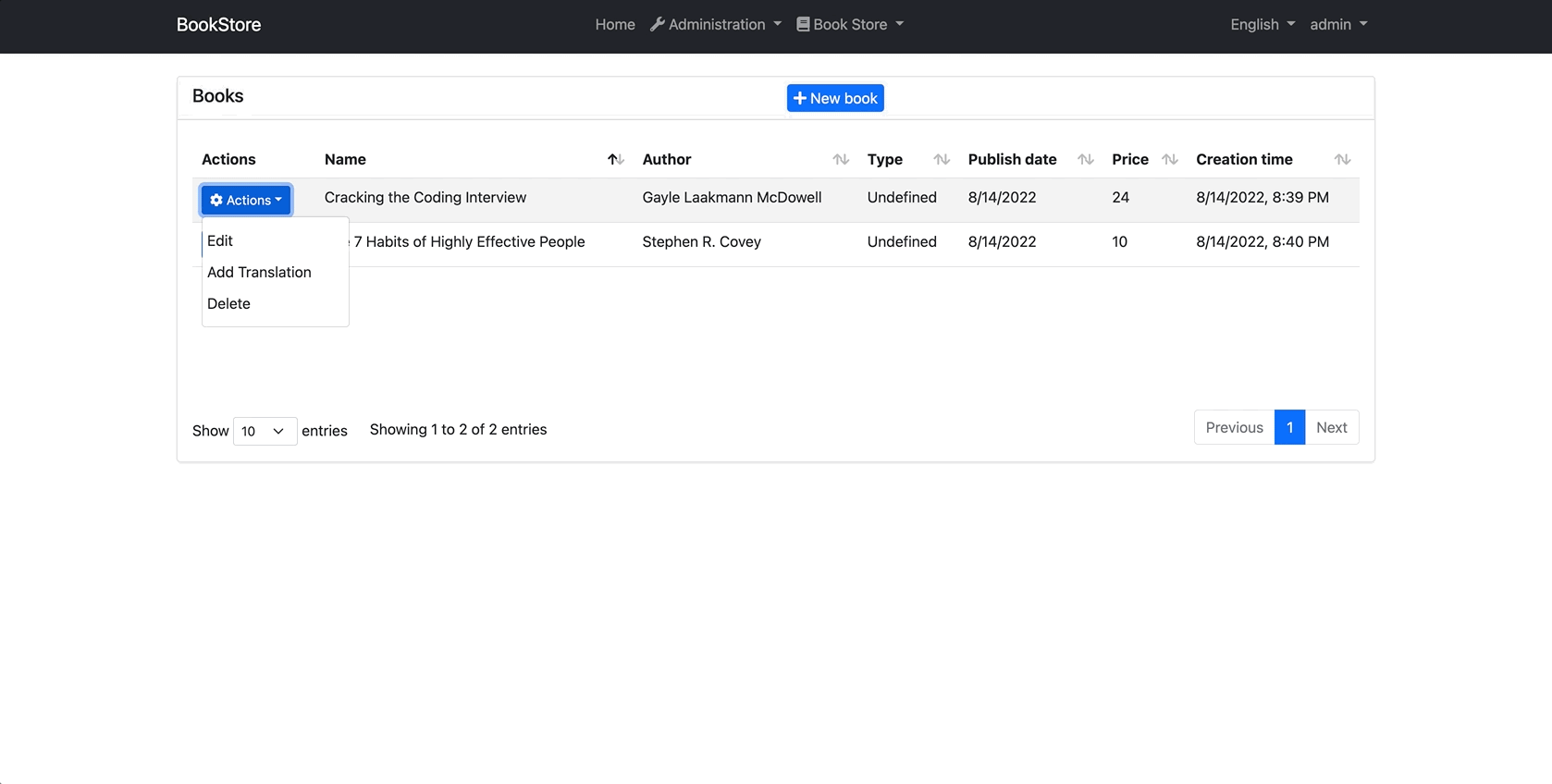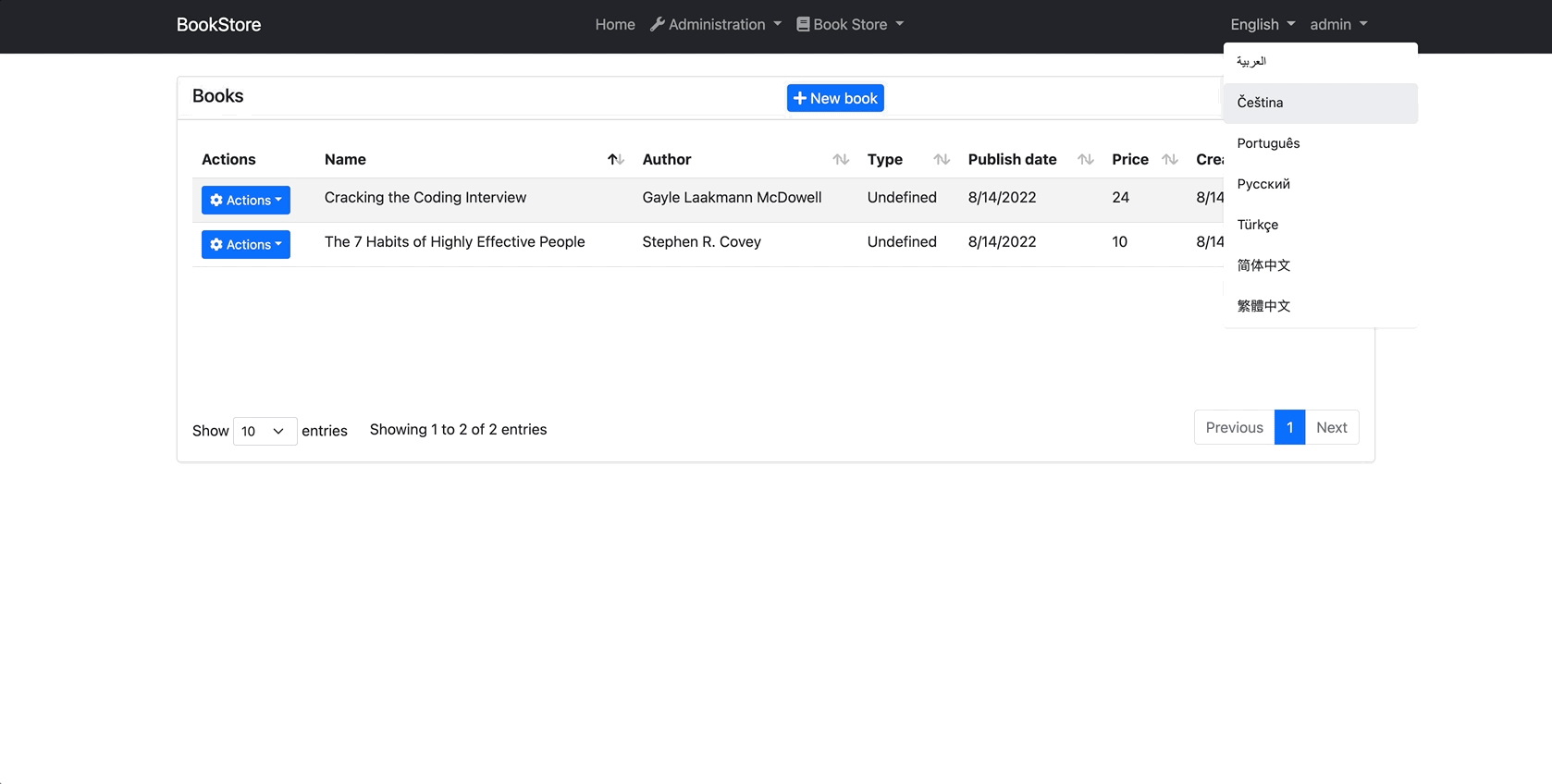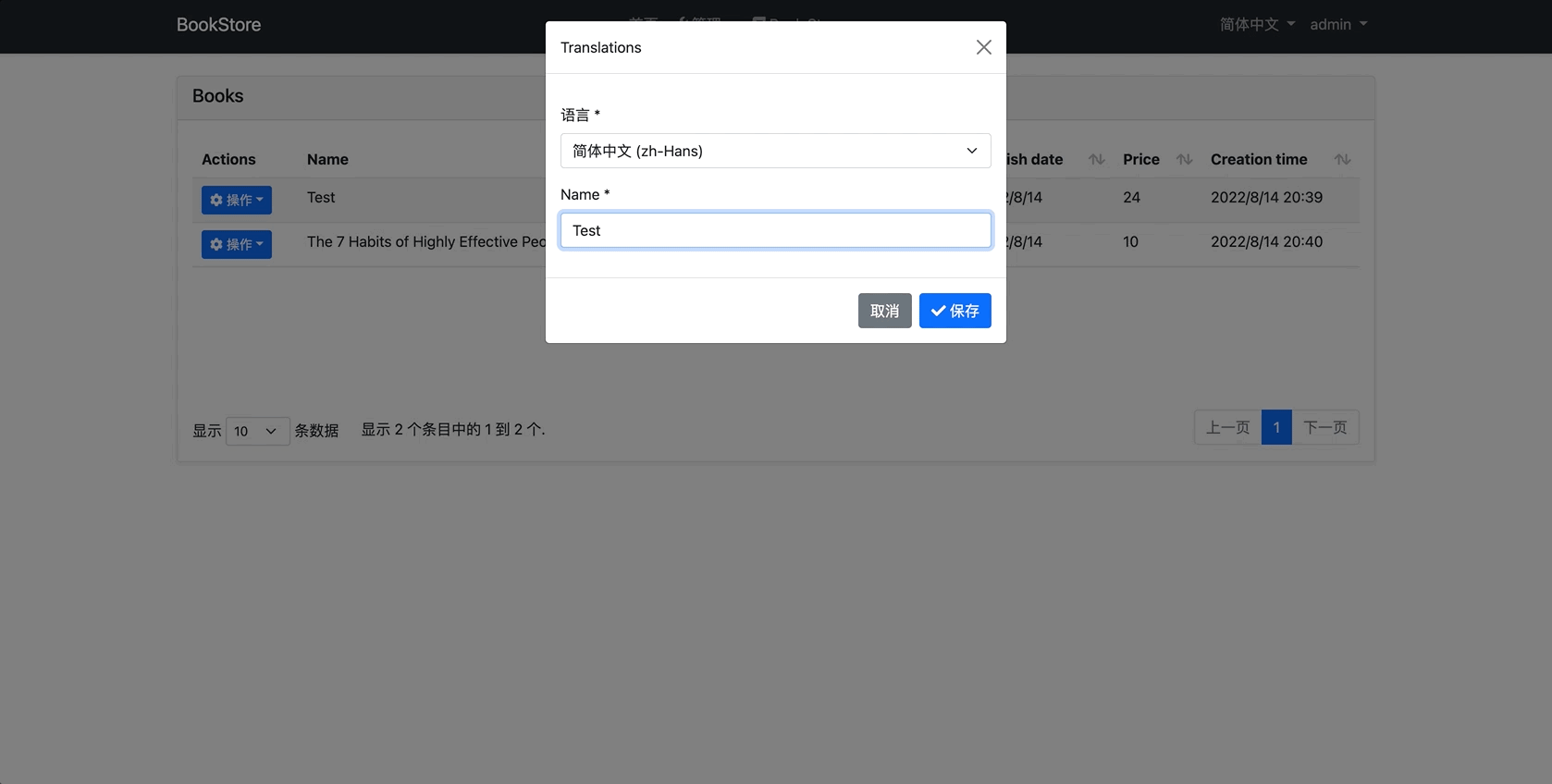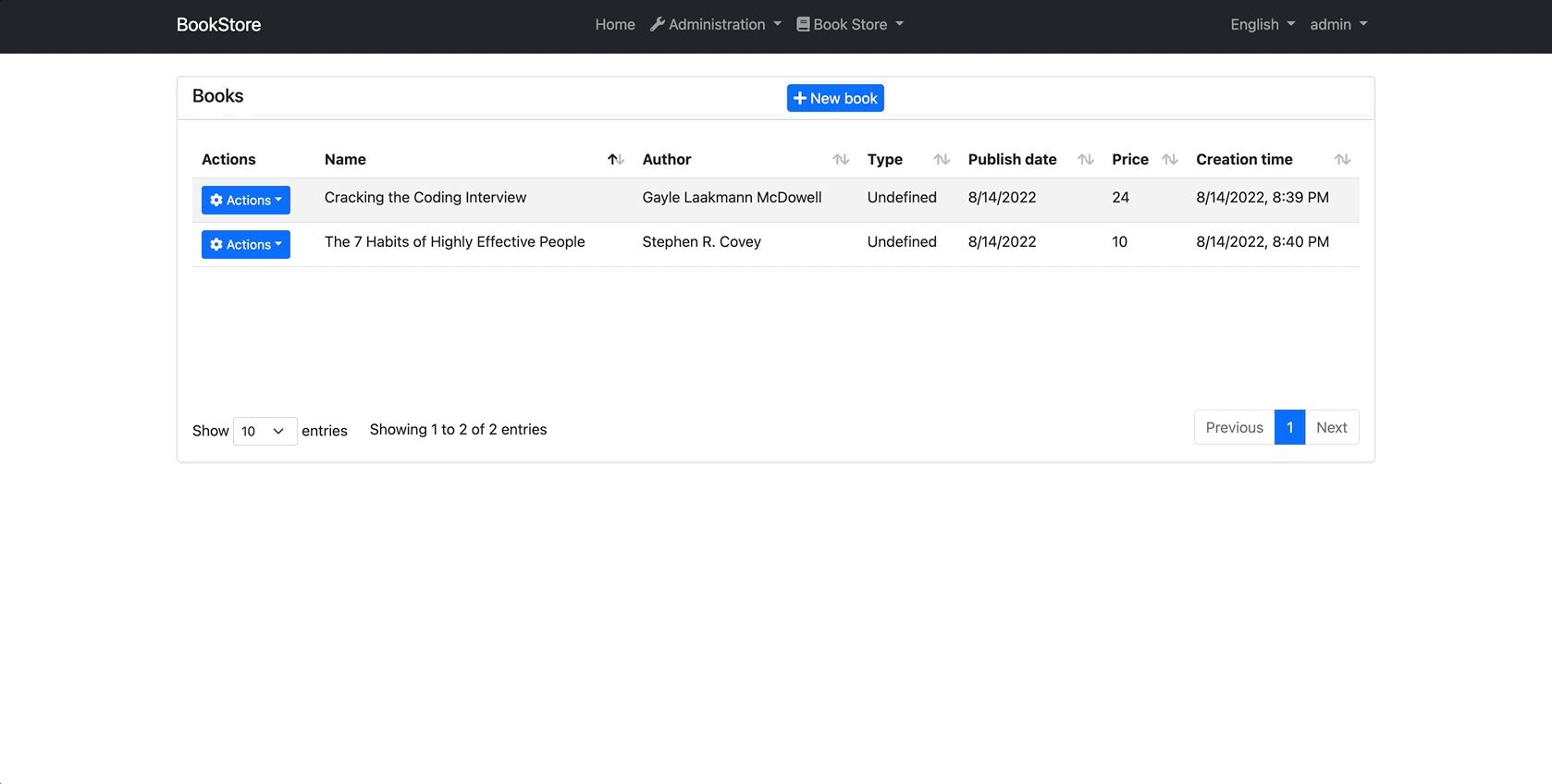
Development
In order to keep the article short and get rid of unrelated information in the article (like defining entities etc.), we'll be using the BookStore example, which is used in the "Web Application Development Tutorial" documentation of ABP Framework and we will make the Book entity as multi-lingual. If you do not want to finish this tutorial, you can find the application here.
Determining the data model
We need a robust, maintainable, and efficient data model to store content in multiple languages.
I read many articles to determine the data model correctly, and as a result, I decided to use one of the many approaches that suit us.
However, as in everything, there is a trade-off here. If you are wondering about the advantages and disadvantages of the model we will implement compared to other models, I recommend you to read this article.
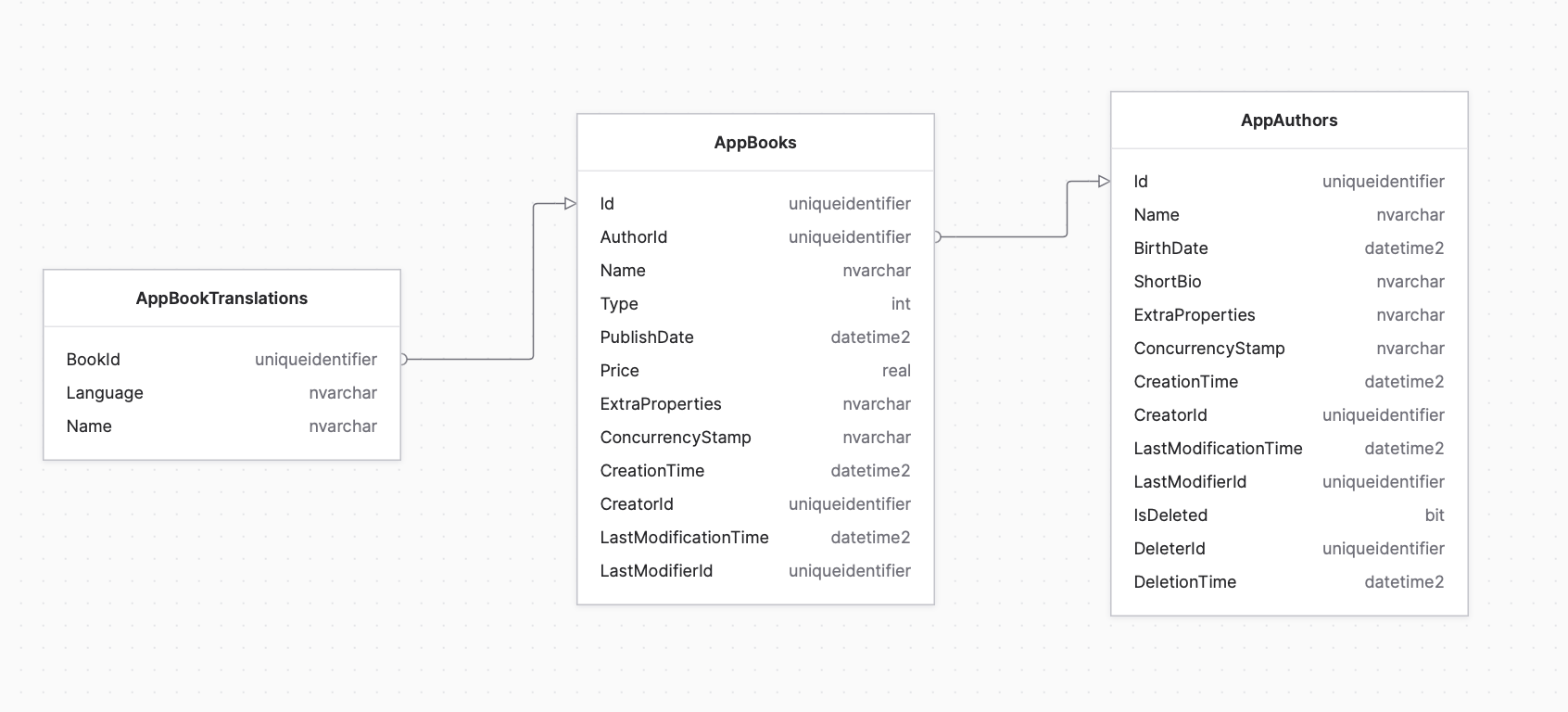
As a result of the tutorial, we already have the Book and Author entities, as an extra, we will just add the BookTranslation.
In the article, we will make the Name property of the Book entity multi-lingual, but the article is independent of the Book entity, you can make the entity you want multi-lingual with similar codes according to your requirements.
Acme.BookStore.Domain.Shared
Create a folder named MultiLingualObjects and create the following interfaces in its contents.
We will use the IObjectTranslation interface to mark the translation of a multi-lingual entity:
public interface IObjectTranslation
{
string Language { get; set; }
}
We will use the IMultiLingualObject<TTranslation> interface to mark multi-lingual entities:
public interface IMultiLingualObject<TTranslation>
where TTranslation : class, IObjectTranslation
{
ICollection<TTranslation> Translations { get; set; }
}
Acme.BookStore.Domain
In the Books folder, create the BookTranslation class as follows:
public class BookTranslation : Entity, IObjectTranslation
{
public Guid BookId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Language { get; set; }
public override object[] GetKeys()
{
return new object[] {BookId, Language};
}
}
BookTranslation contains the Language property, which contains a language code for translation and a reference to the multi-lingual entity. We also have the BookId foreign key to help us know which book is translated.
Implement IMultiLingualObject in the Book class as follows:
public class Book : AuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>, IMultiLingualObject<BookTranslation>
{
public Guid AuthorId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public BookType Type { get; set; }
public DateTime PublishDate { get; set; }
public float Price { get; set; }
public ICollection<BookTranslation> Translations { get; set; }
}
Create a folder named MultiLingualObjects and add the following class inside of this folder:
public class MultiLingualObjectManager : ITransientDependency
{
protected const int MaxCultureFallbackDepth = 5;
public async Task<TTranslation> FindTranslationAsync<TMultiLingual, TTranslation>(
TMultiLingual multiLingual,
string culture = null,
bool fallbackToParentCultures = true)
where TMultiLingual : IMultiLingualObject<TTranslation>
where TTranslation : class, IObjectTranslation
{
culture ??= CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture.Name;
if (multiLingual.Translations.IsNullOrEmpty())
{
return null;
}
var translation = multiLingual.Translations.FirstOrDefault(pt => pt.Language == culture);
if (translation != null)
{
return translation;
}
if (fallbackToParentCultures)
{
translation = GetTranslationBasedOnCulturalRecursive(
CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture.Parent,
multiLingual.Translations,
0
);
if (translation != null)
{
return translation;
}
}
return null;
}
protected TTranslation GetTranslationBasedOnCulturalRecursive<TTranslation>(
CultureInfo culture, ICollection<TTranslation> translations, int currentDepth)
where TTranslation : class, IObjectTranslation
{
if (culture == null ||
culture.Name.IsNullOrWhiteSpace() ||
translations.IsNullOrEmpty() ||
currentDepth > MaxCultureFallbackDepth)
{
return null;
}
var translation = translations.FirstOrDefault(pt => pt.Language.Equals(culture.Name, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase));
return translation ?? GetTranslationBasedOnCulturalRecursive(culture.Parent, translations, currentDepth + 1);
}
}
With MultiLingualObjectManager's FindTranslationAsync method, we get the translated version of the book according to CurrentUICulture. If no translation of culture is found, we return null.
Every thread in .NET has
CurrentCultureandCurrentUICultureobjects.
Acme.BookStore.EntityFrameworkCore
In the OnModelCreating method of the BookStoreDbContext class, configure the BookTranslation as follows:
builder.Entity<BookTranslation>(b =>
{
b.ToTable(BookStoreConsts.DbTablePrefix + "BookTranslations",
BookStoreConsts.DbSchema);
b.ConfigureByConvention();
b.HasKey(x => new {x.BookId, x.Language});
});
I haven't explicitly set up a one-to-many relationship between
BookandBookTranslationhere, but the entity framework will do it for us.
After that, you can just run the following command in a command-line terminal to add a new database migration (in the directory of the EntityFrameworkCore project):
dotnet ef migrations add Added_BookTranslation
This will add a new migration class to your project. You can then run the following command (or run the .DbMigrator application) to apply changes to the database:
dotnet ef database update
Add the following code to the ConfigureServices method of the BookStoreEntityFrameworkCoreModule:
Configure<AbpEntityOptions>(options =>
{
options.Entity<Book>(bookOptions =>
{
bookOptions.DefaultWithDetailsFunc = query => query.Include(o => o.Translations);
});
});
Now we can use WithDetailsAsync without any parameters on BookAppService knowing that Translations will be included.
Acme.BookStore.Application.Contracts
Implement IObjectTranslation in the BookDto class as follows:
public class BookDto : AuditedEntityDto<Guid>, IObjectTranslation
{
public Guid AuthorId { get; set; }
public string AuthorName { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public BookType Type { get; set; }
public DateTime PublishDate { get; set; }
public float Price { get; set; }
public string Language { get; set; }
}
Language property is required to understand which language the translated book name belongs to in the UI.
Create the AddBookTranslationDto class in the Books folder as follows:
public class AddBookTranslationDto : IObjectTranslation
{
[Required]
public string Language { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Name { get; set; }
}
Add the AddTranslationsAsync method to the IBookAppService as follows:
public interface IBookAppService :
ICrudAppService<
BookDto,
Guid,
PagedAndSortedResultRequestDto,
CreateUpdateBookDto>
{
Task<ListResultDto<AuthorLookupDto>> GetAuthorLookupAsync();
Task AddTranslationsAsync(Guid id, AddBookTranslationDto input); // added this line
}
Acme.BookStore.Application
Now, we need to implement the AddTranslationsAsync method in BookAppService and include Translations in the Book entity, for this you can change the BookAppService as follows:
[Authorize(BookStorePermissions.Books.Default)]
public class BookAppService :
CrudAppService<
Book, //The Book entity
BookDto, //Used to show books
Guid, //Primary key of the book entity
PagedAndSortedResultRequestDto, //Used for paging/sorting
CreateUpdateBookDto>, //Used to create/update a book
IBookAppService //implement the IBookAppService
{
private readonly IAuthorRepository _authorRepository;
public BookAppService(
IRepository<Book, Guid> repository,
IAuthorRepository authorRepository)
: base(repository)
{
_authorRepository = authorRepository;
GetPolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Default;
GetListPolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Default;
CreatePolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Create;
UpdatePolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Edit;
DeletePolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Create;
}
public override async Task<BookDto> GetAsync(Guid id)
{
//Get the IQueryable<Book> from the repository
var queryable = await Repository.WithDetailsAsync(); // this line changed
//Prepare a query to join books and authors
var query = from book in queryable
join author in await _authorRepository.GetQueryableAsync() on book.AuthorId equals author.Id
where book.Id == id
select new { book, author };
//Execute the query and get the book with author
var queryResult = await AsyncExecuter.FirstOrDefaultAsync(query);
if (queryResult == null)
{
throw new EntityNotFoundException(typeof(Book), id);
}
var bookDto = ObjectMapper.Map<Book, BookDto>(queryResult.book);
bookDto.AuthorName = queryResult.author.Name;
return bookDto;
}
public override async Task<PagedResultDto<BookDto>> GetListAsync(PagedAndSortedResultRequestDto input)
{
//Get the IQueryable<Book> from the repository
var queryable = await Repository.WithDetailsAsync(); // this line changed
//Prepare a query to join books and authors
var query = from book in queryable
join author in await _authorRepository.GetQueryableAsync() on book.AuthorId equals author.Id
select new {book, author};
//Paging
query = query
.OrderBy(NormalizeSorting(input.Sorting))
.Skip(input.SkipCount)
.Take(input.MaxResultCount);
//Execute the query and get a list
var queryResult = await AsyncExecuter.ToListAsync(query);
//Convert the query result to a list of BookDto objects
var bookDtos = queryResult.Select(x =>
{
var bookDto = ObjectMapper.Map<Book, BookDto>(x.book);
bookDto.AuthorName = x.author.Name;
return bookDto;
}).ToList();
//Get the total count with another query
var totalCount = await Repository.GetCountAsync();
return new PagedResultDto<BookDto>(
totalCount,
bookDtos
);
}
public async Task<ListResultDto<AuthorLookupDto>> GetAuthorLookupAsync()
{
var authors = await _authorRepository.GetListAsync();
return new ListResultDto<AuthorLookupDto>(
ObjectMapper.Map<List<Author>, List<AuthorLookupDto>>(authors)
);
}
public async Task AddTranslationsAsync(Guid id, AddBookTranslationDto input)
{
var queryable = await Repository.WithDetailsAsync();
var book = await AsyncExecuter.FirstOrDefaultAsync(queryable, x => x.Id == id);
if (book.Translations.Any(x => x.Language == input.Language))
{
throw new UserFriendlyException($"Translation already available for {input.Language}");
}
book.Translations.Add(new BookTranslation
{
BookId = book.Id,
Name = input.Name,
Language = input.Language
});
await Repository.UpdateAsync(book);
}
private static string NormalizeSorting(string sorting)
{
if (sorting.IsNullOrEmpty())
{
return $"book.{nameof(Book.Name)}";
}
if (sorting.Contains("authorName", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
return sorting.Replace(
"authorName",
"author.Name",
StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase
);
}
return $"book.{sorting}";
}
}
Create the MultiLingualBookObjectMapper class as follows:
public class MultiLingualBookObjectMapper : IObjectMapper<Book, BookDto>, ITransientDependency
{
private readonly MultiLingualObjectManager _multiLingualObjectManager;
private readonly ISettingProvider _settingProvider;
public MultiLingualBookObjectMapper(
MultiLingualObjectManager multiLingualObjectManager,
ISettingProvider settingProvider)
{
_multiLingualObjectManager = multiLingualObjectManager;
_settingProvider = settingProvider;
}
public BookDto Map(Book source)
{
var translation = AsyncHelper.RunSync(() =>
_multiLingualObjectManager.FindTranslationAsync<Book, BookTranslation>(source));
return new BookDto
{
Id = source.Id,
AuthorId = source.AuthorId,
Type = source.Type,
Name = translation?.Name ?? source.Name,
PublishDate = source.PublishDate,
Price = source.Price,
Language = translation?.Language ?? AsyncHelper.RunSync(() => _settingProvider.GetOrNullAsync(LocalizationSettingNames.DefaultLanguage)),
CreationTime = source.CreationTime,
CreatorId = source.CreatorId,
LastModificationTime = source.LastModificationTime,
LastModifierId = source.LastModifierId
};
}
public BookDto Map(Book source, BookDto destination)
{
return default;
}
}
To map the multi-lingual Book entity to BookDto, we implement custom mapping using the IObjectMapper<TSource, TDestination> interface. If no translation is found, default values are returned.
So far we have created the entire infrastructure. We don't need to change anything in the UI, if there is a translation according to the language chosen by the user, the list view will change. However, I want to create a simple modal where we can add new translations to an existing book in order to see what we have done.
Acme.BookStore.Web
Create a new razor page named AddTranslationModal in the Books folder as below.
View
@page
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.TagHelpers
@using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.Bootstrap.TagHelpers.Modal
@model Acme.BookStore.Web.Pages.Books.AddTranslationModal
@{
Layout = null;
}
<form asp-page="/Books/AddTranslationModal">
<abp-modal>
<abp-modal-header>Translations</abp-modal-header>
<abp-modal-body>
<abp-input asp-for="Id"></abp-input>
<abp-select asp-for="@Model.TranslationViewModel.Language" asp-items="Model.Languages" class="form-select">
<option selected value="">Pick a language</option>
</abp-select>
<abp-input asp-for="TranslationViewModel.Name"></abp-input>
</abp-modal-body>
<abp-modal-footer buttons="@(AbpModalButtons.Cancel | AbpModalButtons.Save)"></abp-modal-footer>
</abp-modal>
</form>
Model
public class AddTranslationModal : BookStorePageModel
{
[HiddenInput]
[BindProperty(SupportsGet = true)]
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public List<SelectListItem> Languages { get; set; }
[BindProperty]
public BookTranslationViewModel TranslationViewModel { get; set; }
private readonly IBookAppService _bookAppService;
private readonly ILanguageProvider _languageProvider;
public AddTranslationModal(
IBookAppService bookAppService,
ILanguageProvider languageProvider)
{
_bookAppService = bookAppService;
_languageProvider = languageProvider;
}
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
Languages = await GetLanguagesSelectItem();
TranslationViewModel = new BookTranslationViewModel();
}
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
await _bookAppService.AddTranslationsAsync(Id, ObjectMapper.Map<BookTranslationViewModel, AddBookTranslationDto>(TranslationViewModel));
return NoContent();
}
private async Task<List<SelectListItem>> GetLanguagesSelectItem()
{
var result = await _languageProvider.GetLanguagesAsync();
return result.Select(
languageInfo => new SelectListItem
{
Value = languageInfo.CultureName,
Text = languageInfo.DisplayName + " (" + languageInfo.CultureName + ")"
}
).ToList();
}
public class BookTranslationViewModel
{
[Required]
[SelectItems(nameof(Languages))]
public string Language { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
Then, we can open the BookStoreWebAutoMapperProfile class and define the required mapping as follows:
CreateMap<AddTranslationModal.BookTranslationViewModel, AddBookTranslationDto>();
Finally, change the content of index.js in the Books folder as follows:
$(function () {
var l = abp.localization.getResource('BookStore');
var createModal = new abp.ModalManager(abp.appPath + 'Books/CreateModal');
var editModal = new abp.ModalManager(abp.appPath + 'Books/EditModal');
var addTranslationModal = new abp.ModalManager(abp.appPath + 'Books/AddTranslationModal'); // added this line
var dataTable = $('#BooksTable').DataTable(
abp.libs.datatables.normalizeConfiguration({
serverSide: true,
paging: true,
order: [[1, "asc"]],
searching: false,
scrollX: true,
ajax: abp.libs.datatables.createAjax(acme.bookStore.books.book.getList),
columnDefs: [
{
title: l('Actions'),
rowAction: {
items:
[
{
text: l('Edit'),
visible: abp.auth.isGranted('BookStore.Books.Edit'),
action: function (data) {
editModal.open({ id: data.record.id });
}
},
{
text: l('Add Translation'), // added this action
visible: abp.auth.isGranted('BookStore.Books.Edit'),
action: function (data) {
addTranslationModal.open({ id: data.record.id });
}
},
{
text: l('Delete'),
visible: abp.auth.isGranted('BookStore.Books.Delete'),
confirmMessage: function (data) {
return l(
'BookDeletionConfirmationMessage',
data.record.name
);
},
action: function (data) {
acme.bookStore.books.book
.delete(data.record.id)
.then(function() {
abp.notify.info(
l('SuccessfullyDeleted')
);
dataTable.ajax.reload();
});
}
}
]
}
},
{
title: l('Name'),
data: "name"
},
{
title: l('Author'),
data: "authorName"
},
{
title: l('Type'),
data: "type",
render: function (data) {
return l('Enum:BookType:' + data);
}
},
{
title: l('PublishDate'),
data: "publishDate",
render: function (data) {
return luxon
.DateTime
.fromISO(data, {
locale: abp.localization.currentCulture.name
}).toLocaleString();
}
},
{
title: l('Price'),
data: "price"
},
{
title: l('CreationTime'),
data: "creationTime",
render: function (data) {
return luxon
.DateTime
.fromISO(data, {
locale: abp.localization.currentCulture.name
}).toLocaleString(luxon.DateTime.DATETIME_SHORT);
}
}
]
})
);
createModal.onResult(function () {
dataTable.ajax.reload();
});
editModal.onResult(function () {
dataTable.ajax.reload();
});
$('#NewBookButton').click(function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
createModal.open();
});
});
Conclusion
With a multi-lingual application, you can expand your market share, but if not designed well, may your application will be unusable. So, I've tried to explain how to design a sustainable multi-lingual entity in this article.
Source Code
You can find source code of the example solution used in this article here.




Comments
Engincan VESKE 126 weeks ago
Great article!
Kirti Kulkarni 126 weeks ago
Yes much needed article ! I had implemented similar in aspnetzero.
Serdar Genc 125 weeks ago
nice article, thanks
injy93@gmail.com 112 weeks ago
Hello useful article ! Is there a way to do this for extend existing entities of a depended module? I try to add a multilingual field:[Description] to the identity Role entity...
Berkan Sasmaz 111 weeks ago
Thank you. Since this will require big changes, my suggestion is that you can add the module with the source code and update the related entities, and others as in the article. This has its downsides, but if I were in your situation, I would choose this way.
wenceslao.leon@mgti.cl 101 weeks ago
thank you, could it be implemented in a multitenant solution?